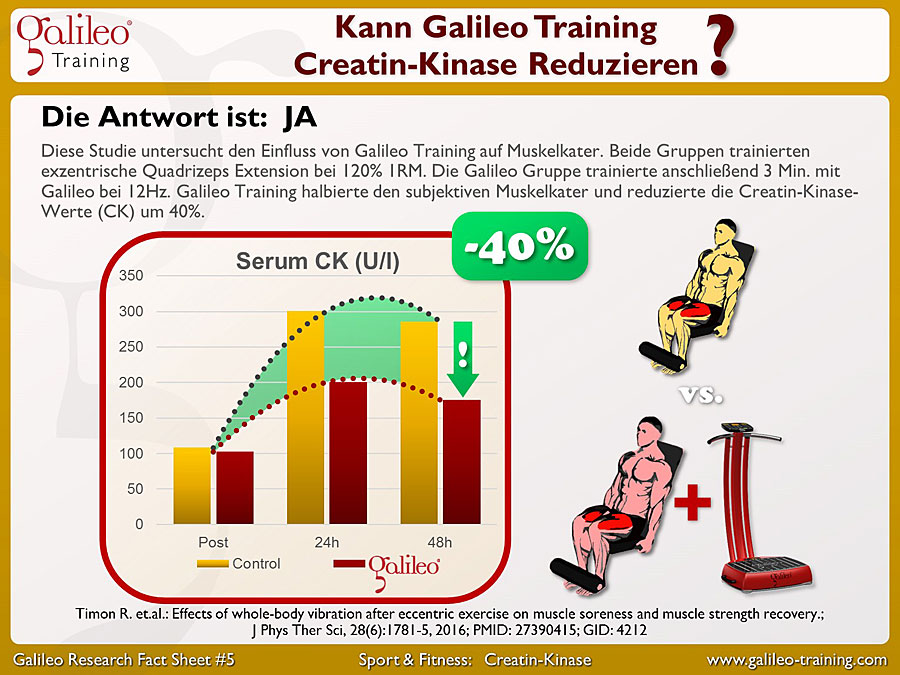
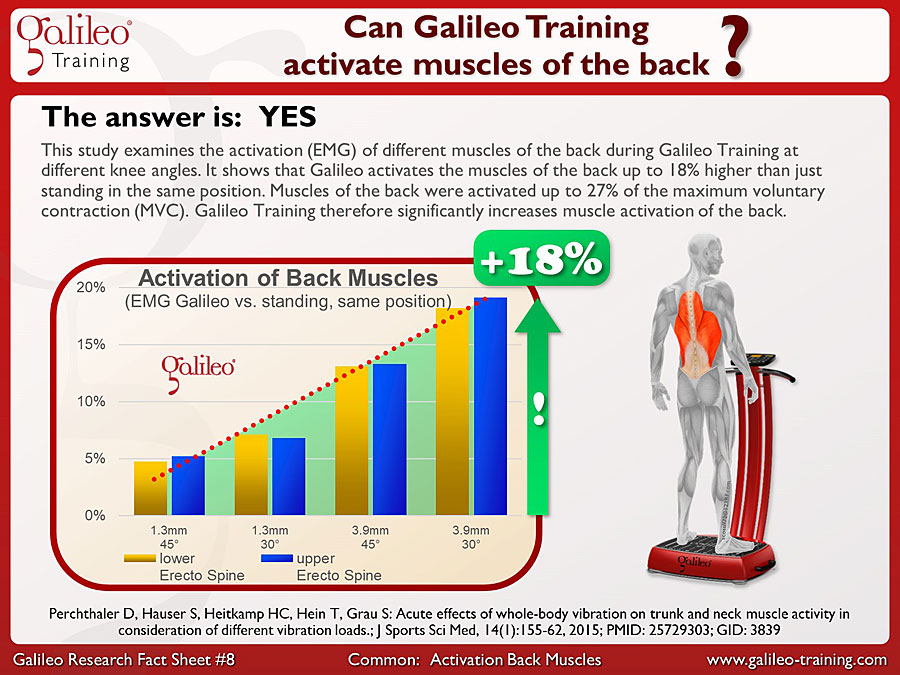
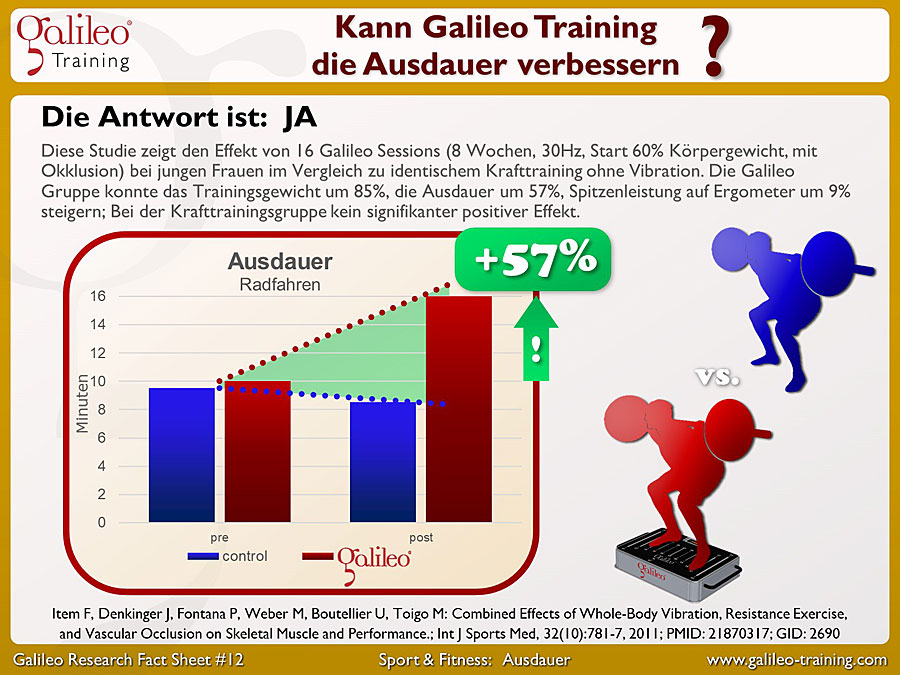
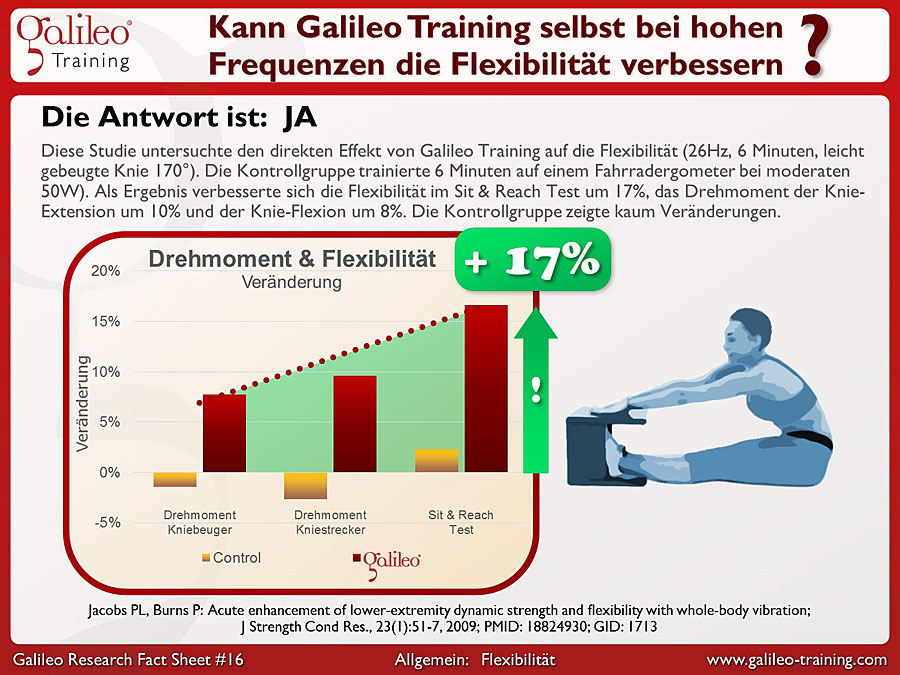
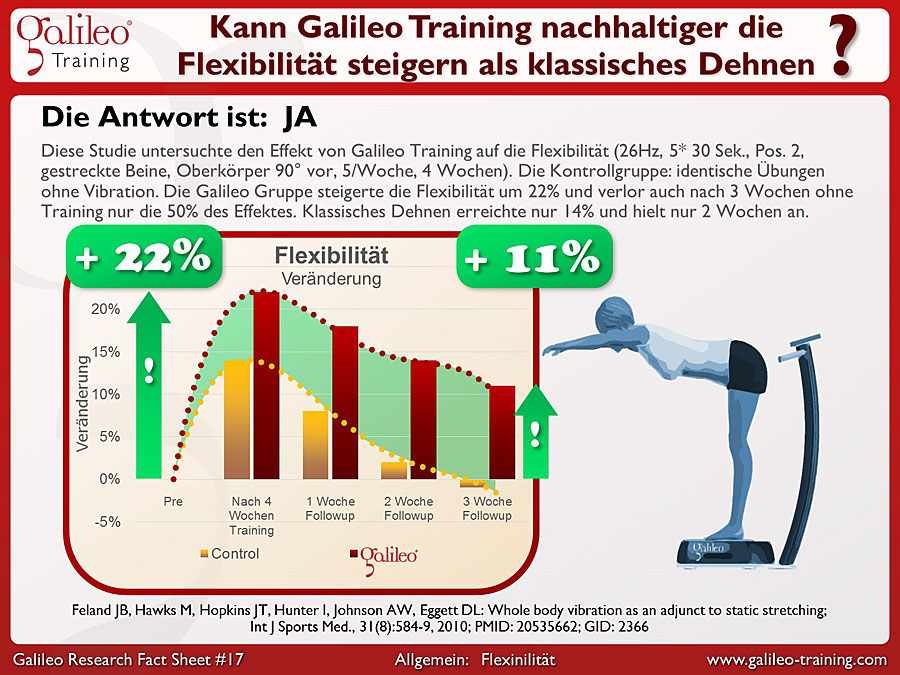
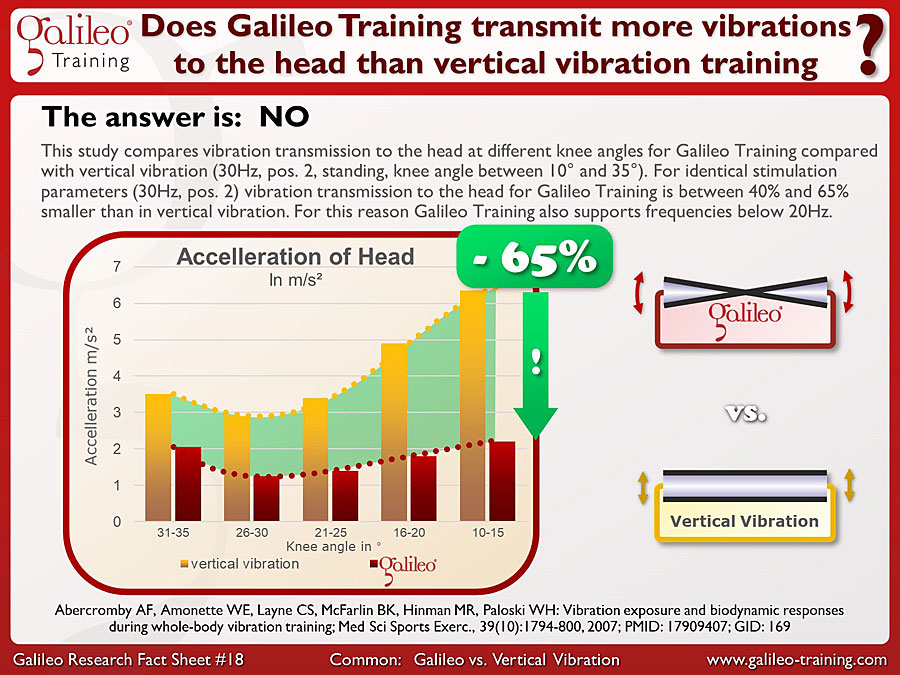
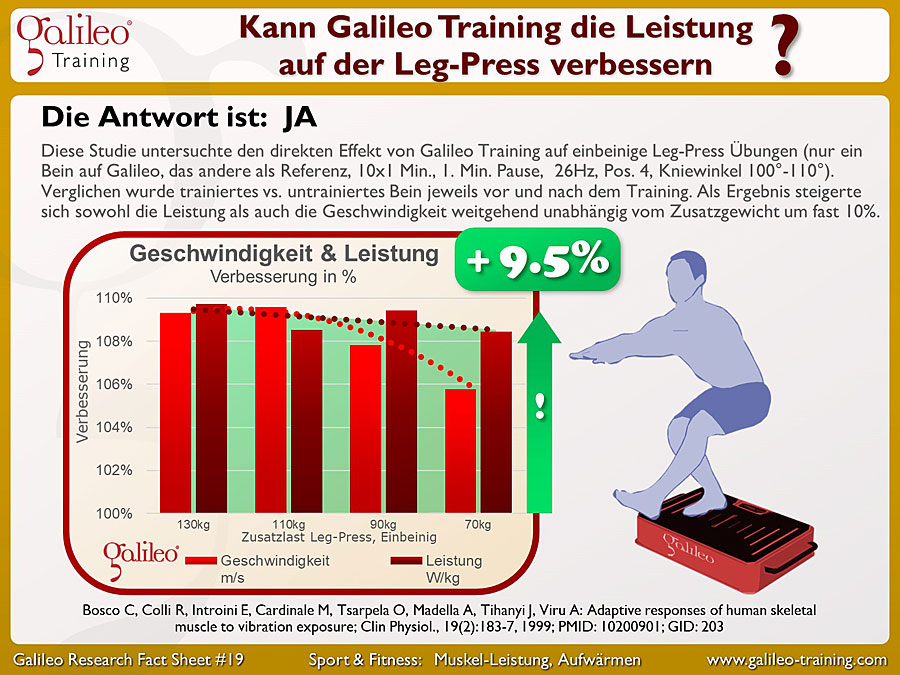
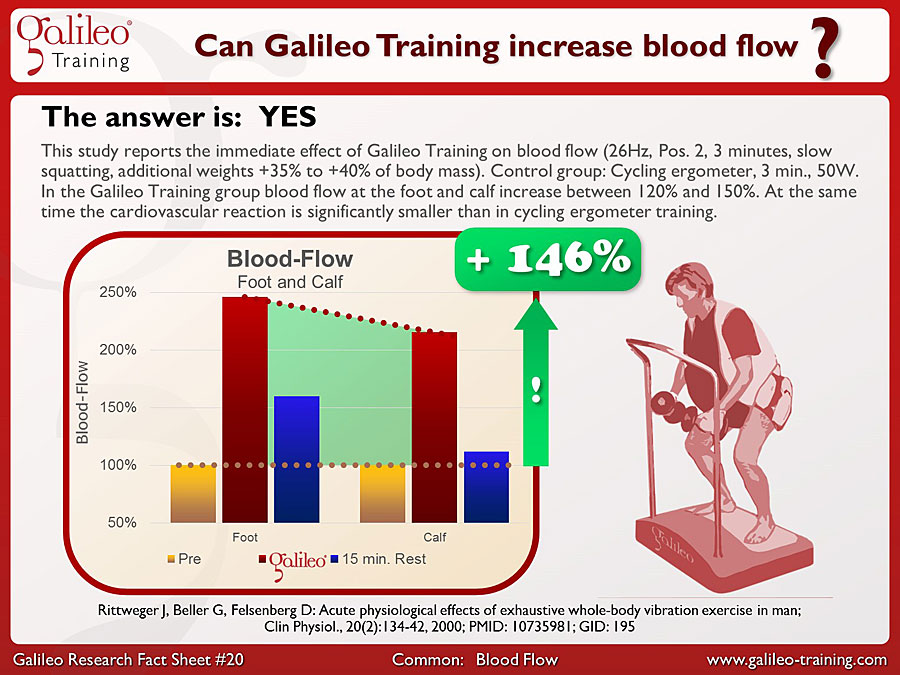
Galileo® Training
Relationship between frequency and training goal
Regardless of the stimulation frequency, blood flow and microcirculation within the activated body parts are considerably stimulated; in addition, an improvement in flexibility and thus energy storage capacity in the tendon-muscle complex can be made possible.
The stimulation frequency also has a direct influence on the effects of Galileo Training and must therefore be selected according to the training goal desired for the individual exercise. It should be noted that the information given below may vary individually by a few hertz, e.g. depending on the predisposition and condition of the user.
Depending on the frequency range, the muscle or the body can react in different ways.
The following three frequency ranges of Galileo Training are therefore not arbitrarily chosen, but are directly derived from neurology and muscle physiology (biological & mechanical properties of the muscle and its neuronal control).

Do you have questions about our products or would you like to purchase a product?
Get advice from our experts. Simply arrange a phone-call to answer your questions.
Medium frequencies (approx. 12-20 hertz)
The training goal at medium frequencies of 12 to 20 hertz (oscillations per second) is muscle function as such.
Galileo® Training effects at 12-20 Hz
- Improvement of muscle function and coordination
- Muscle relaxation
- Stretching of the muscle and tendon system
- Increasing mobility
- Relaxation
- Muscle relaxation, reduction of muscle soreness
- Muscle length training
- Fascia training
- Improved Blood-flow
- Increased Metabolism

High repetition rates
At a stimulation frequency of, for example, 15 hertz, the time between two reflex cycles is about 67 milliseconds (thousandths of a second). After the reflex-controlled contraction, the remaining time until the next contraction is thus sufficient for the muscle to relax again (the average physiological time for a complete contraction/relaxation cycle, on the other hand, is about 50 milliseconds).
This is particularly important when the basic functions of the muscle, namely both contraction and relaxation ability as well as coordination shall be effectively challenged. Due to the large number of repetitions (e.g. 3 minutes Galileo training at 20 Hertz = 3600 cycles per leg, i.e. a total of 7200 steps), the improvement of muscle functions can be achieved considerably faster than with most other training methods such as resistance training.

Relaxation
The reflex muscle contractions that can be triggered by Galileo can extend all the way up the back, depending on the posture. Galileo effectively helps to relax muscles, stretch the shortened muscle-tendon apparatus and at the same time significantly improve coordination within the muscle chain. This is why Galileo Training can improve flexibility, stretching ability and posture in the long term. After Galileo Training, many users feel good, walk "like on air", are refreshed and full of energy - very good prerequisites for an all-round good body feeling.

Reflective activation of the muscle chain
A decisive factor is that muscle activity during Galileo Training is not controlled by the user's will, but is reflex-based and therefore largely uninfluenced by the user's volition. This can ensure that the control circuits consisting of muscle/ligaments/tendons/cartilage nerves can improve independently. At the same time (depending on the posture) the closed muscle chain and thus its coordination is stimulated.
A crucial prerequisite for improving coordination using Galileo Training is that the entire muscle chain can be stimulated in a physiologically meaningful pattern, similar to that of the human gait. Therefore, we also speak of a mechano-stimulation of the musculature or the neuromuscular system.
High frequencies (approx. 25-40 hertz)
High frequencies between 25 and 40 hertz are used in Galileo Training to build muscle, increase muscle power and endurance.
Galileo® Training Effekte bei 25-40 Hz
- Increasing muscle power (energetic expenditure)
- Increasing muscle strength or recovery after immobilisation
- Increasing muscle mass
- Increasing endurance
- Body forming
- Promotion of blood circulation
- Fascia training

Efficient exhaustion
At high frequencies, there is insufficient time for the muscle to achieve complete relaxation within the short time between two cycles. Rather, the muscle is always forced to contract again just when it is about to relax again or is already partially relaxed. As a result, more and more muscle fibres / motor units have to be recruited.

Coordination & Training
In addition, inter- and intramuscular coordination in particular can be improved with greater forces within very short time spans, which ultimately results in an increase in muscle power.
Many years of experience with Galileo Training, especially with top athletes, show that a maximum frequency of up to 33 Hz is sufficient for most users. However, for ambitious amateur sports people, for example, and especially for athletes, frequencies of up to 36 Hz or 40 Hz can achieve an even higher output.

Impulses for Muscle & Bone
The reflex muscle contractions that can be triggered by Galileo can extend all the way up the back, depending on the posture. Depending on the selected training frequency, the training can be extremely intensive and the muscles can be quickly exhausted. Precisely this exertion is the greatest stimulus for building up and increasing the muscle power. Strong muscles are not only crucial for fitness and sport, but also for preventing falls in old age, for example. Large muscular forces acting on the bone also promote bone preservation or even bone formation.
Low frequencies (approx. 5-10 Hertz)
Low frequencies between 5 and 10 hertz are used for balance and mobilisation and demand voluntary access (especially neurological areas of application).
Galileo® Training effects at 5-10 Hz
- Mobility
- Muscle relaxation
- Cool-Down
- Balance training

Voluntary muscle activation
At low frequencies, the movement of the Galileo systems is not fast enough to trigger significant stretch reflexes. Due to the dominant voluntary compensation of the rocking movement, low frequencies can therefore be used in particular to relax, but also to improve balance or proprioception. They become apparent in the body by a significantly increased movement of the hips, for example. Due to the comparatively large range of motion with simultaneously low muscle activation, low frequencies are therefore also well suited for mobilisation.

Relaxation & Cool-Down
Muscle activation is significantly lower at low frequencies than at higher frequencies. The application therefore feels much more passive, similar to a massage. Therefore, this frequency range is also suitable for relaxation after intensive training.

Balance training
At low frequencies, the stretch reflex is largely inactive and therefore cannot have a supportive effect. This demands voluntary access to the muscles, which is particularly noticeable during balance exercises. This effect can be further enhanced by the optional wobble function (random, stochastic frequency change) and thus comes much closer to unpredictable everyday situations.

Do you have questions about our products or would you like to purchase a product?
Get advice from our experts. Simply arrange a phone-call to answer your questions.
You would like to know more about the background of Galileo® Training ?
Choose one of the following topics:
Galileo® active principle side alternation
Galileo® Basic Exercises
Galileo® Training Fact sheets
Research results on the application of
Galileo® Training. Get fit - stay fit.
Let Galileo® Training convince you!
Numerous scientific publications show the effectiveness of Galileo Training.
Benefit from the knowledge gained from over 25 years of experience and from over 500 scientific publications on Galileo worldwide.